#98- The MSME Credit Chasm
How India Stack & OCEN can enhance credit, and provide a lifeline for MSMEs in India - Part 1
Dear Readers,
Wishing you Happy Diwali!
A lot has changed since I last posted. After 5 years of investing in public equities, early stage ventures, and venture funds, I moved on from my role at Malpani Ventures at the end of September - taking with me a ton of blessings, learnings, and friends for life.
I’ve since joined Siana Capital at their Bombay office to help build our Fund 2. At Siana, we fund Deep Tech in India with a focus on IP-led B2B businesses in emerging technologies within healthcare, biotech, software, financial services, climate, etc.
Although my focus at my previous firm was more on SaaS, Deep Tech is not new to me. I’ve funded the likes of Nesa Medtech which is building an innovative, scarless, minimally invasive surgical treatment for uterine fibroids; Mestastop which is creating a platform to help pharmaceutical companies discover drugs which can stop the spread, and eventually cure cancer; and Biomoneta which is one of the world’s foremost air decontamination and purification device.
At Siana I wish to continue doing more of the same - but also get a ringside view of how to raise, build, and run a fund, something I’d like to do myself eventually.
If you’d like to catch up sometime, please write to me below.
The MSME sector is close to my heart. Belonging to a business family, I’ve seen this space evolve closely . India’s MSME sector is a key driver of socio-economic progress. It contributes to 29% of India’s GDP, 36% of India’s manufacturing output, and provides employment to ~11cr of India’s 41cr workforce.
Yet, this Ratna is hardly rewarded. In spite of its critical significance, the MSME sector in India continues to grapple with a pervasive challenge – insufficient access to credit. It has been able to avail only between Rs 20-25 lac crores out of India’s outstanding credit of almost Rs 150 lac crores (merely 16% of the pie). These MSMEs face significant obstacles while accessing credit - credit is either unavailable, inaccessible, or expensive. Having experienced it first-hand, I realize how crippling it is for a small business to operate without credit.
The total MSME credit demand in India is considered to be $500bn out of which only $200bn is met by formal credit. The rest 60% demand is served by informal channels charging exorbitantly high interest rates; almost double to what the formal sector charges. The formal lending that is being done is also one-sided, currently ~4% of all MSMEs capture ~75% of the total credit lent out to MSMEs. These 4% include the likes of large manufacturers, distributors, upscale retail stores leaving out MSMEs like your neighbourhood kirana shop.
Shubham Gupta writes ‘On the importance of lending for India’
The government, recognizing this bottleneck, implemented initiatives aimed at infusing capital into MSMEs like:
Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme
Credit Guarantee Trust Fund for MSMEs, and
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana
Despite these efforts, a formidable credit gap endures, with some estimates pegging it at a INR 25 lac crores with others even higher. While the correct number is yet to be ascertained, we are aware the number is magnanimous nonetheless. Government programs, although well-intentioned, seem to falter in closing this significant void. This unresolved credit gap emerges as a substantial roadblock, hindering the growth not only of the MSME sector, which employs 11 cr individuals, but also casting a shadow over the broader Indian economy.
However, recent advances in India's digital infrastructure offer a promising solution to enhance MSMEs' access to credit. The Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN), utilizing the India Stack APIs, has the potential & promise to narrow the MSME credit gap and foster collaboration between lenders and borrowers.
Using tech to help MSMEs
India's OCEN emerges as a game-changer for MSMEs. This platform hopes to deliver a standardized and simplified approach to accessing credit from a multitude of lenders.
The primary goal? To drive financial inclusion, slash operational costs, reduce turnaround time, and stimulate healthy competition among lenders, all while upholding the principles of responsible lending.
OCEN, at its core, is more than a platform; it's a catalyst for empowering borrowers and optimizing lending operations. By seamlessly integrating with the India Stack, it not only demystifies but revolutionizes the lending process for MSMEs. Embedded credit becomes a crucial component, acting as an essential element which streamlines and accelerates access to much-needed funds for businesses and individuals alike.
In essence, OCEN is not just a technological innovation; it's a force that democratizes financial services, transforming the way credit is accessed and managed. As we stand at the cusp of its widespread implementation, we can redefine the narrative of financial empowerment for the MSME sector in India. To understand OCEN we first need to understand the India Stack which has been a decade in the making.
Layers of India Stack
India Stack, a behemoth of open APIs, is the spinal cord of this interconnected landscape, sitting comfortably between digital innovation and financial inclusivity. At its core, India Stack stands tall on three pillars—Identity, Payments, and Data—each a vital contributor to the nation's digital change.
Identity Layer: Aadhaar's Dominance
Aadhaar empowers over a billion Indians with a unique and verifiable digital identity. This not only eases access to government services but also spearheads financial inclusion, catalyzing the opening of bank accounts and the adoption of digital financial services.
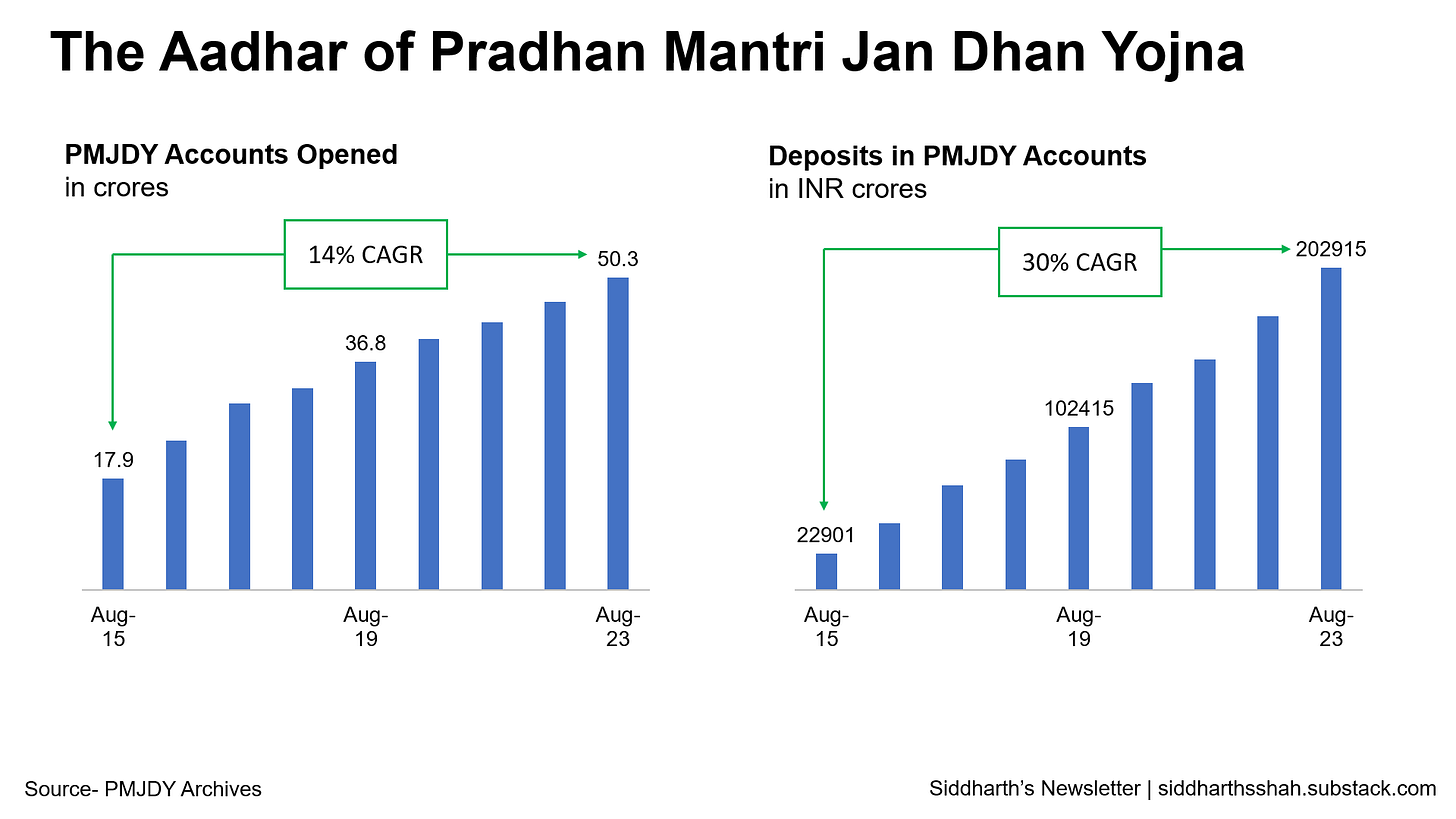
Case in point - Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojna (PMJDY) led account opening for crores of Indians for Direct Benefit Transfers using Aadhar. Account opening has grown at a CAGR of 14% over the 8-year period while deposits in accounts have grown at a CAGR of over 30%.
Payments Layer: UPI's Resonance
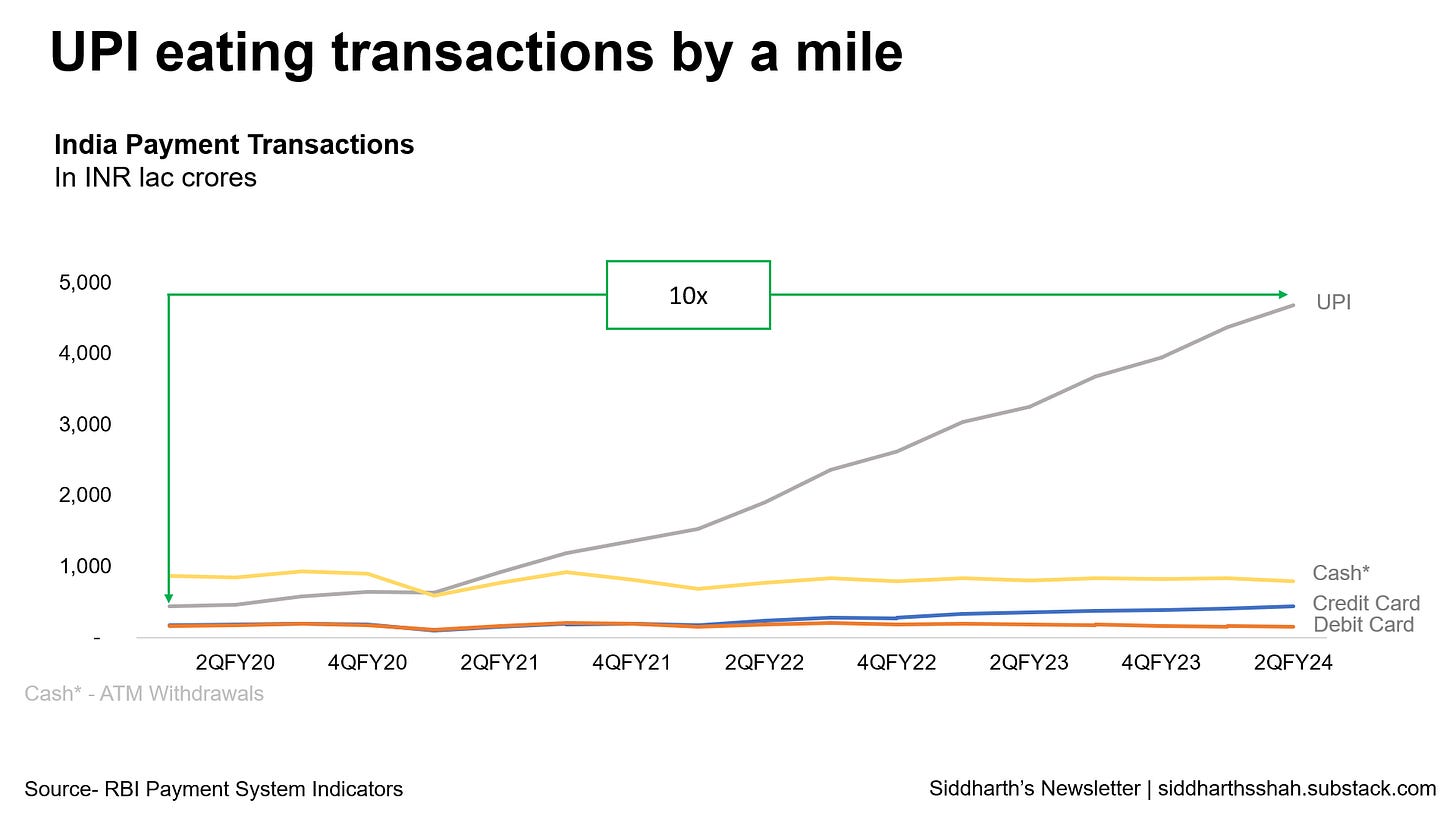
Unified Payments Interface (UPI), the maestro of digital transactions, has taken center stage in the Payments layer. Revolutionizing the financial landscape, UPI facilitates seamless and instant money transfers via mobile phones, weaving itself into the fabric of everyday transactions. Its ubiquity and user-friendliness make it the quintessential digital payment solution. From kirana to airline tickets - UPI is accepted everywhere.
Data Layer: Empowering Through DEPA
The Data layer, governed by the Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture (DEPA), brought a new era of individual control over data. DEPA's consent managers, acting as custodians, ensure secure and encrypted data transfers, keeping user privacy in mind. The Account Aggregator, a financial data consent manager under the Reserve Bank of India's watchful eye, stands as a fortress, granting secure digital access to financial information with the user's explicit consent.
OCEN's Unbundling
India's fintech landscape, sculpted by India Stack, now braces for the next frontier—the Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN). This paradigm shift in digital lending unbundles traditional frameworks, ushering in a future defined by precision and efficiency in lending practices.
In the India Stack, where APIs serve as the alchemist's potion, India undergoes a metamorphosis, transforming into a digital crusade. The journey from Aadhaar's identity empowerment to UPI's financial ubiquity, culminating in DEPA's data governance, narrates a progress of India’s dominant use of technology to tackle problems. As OCEN promises to take the reins, the narrative continues—an unfolding chapter in India's relentless pursuit of a digitally inclusive future.
In my next post, I will discuss embedded finance and how OCEN can change the way it works for MSMEs.